Learning reported speech rules can feel like decoding secret grammar rituals — but it’s simpler than you think. In this guide, we’ll break down how reported speech works, when to use it, and how to avoid common mistakes. Ready to stop quoting like a robot? Let’s get into it.
In this guide, we’ll unpack reported speech — a grammatical tool that lets you pass along what someone else said without quoting them directly. You’ll explore the key reported speech rules, how to convert statements naturally, and avoid the typical blunders that make you sound like an emotionally repressed grammar bot.
Let’s decode the mystery.
What Is Reported Speech and Why It Matters
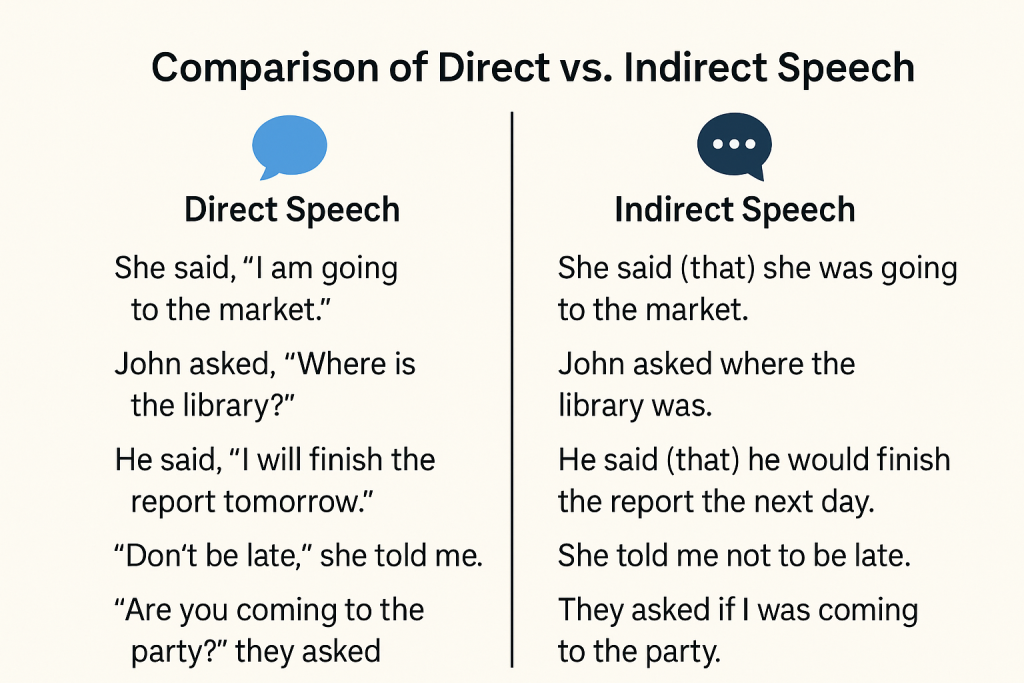
Direct speech is when you quote exactly what someone said: “I love chocolate,” she said. Reported speech, or indirect speech, is when you tell someone what another person said, but with a few grammatical upgrades: She said that she loved chocolate. See what happened there? Grammar sorcery.
Core Differences
- Tense changes: Present becomes past, because your sentence needs to age like fine cheese.
- Pronouns adjust: Because no one wants to accidentally report themselves.
- Time expressions update: “Today” becomes “that day,” because grammar loves drama.
Examples:
- “I am hungry” → He said he was hungry.
- “We will call you” → They said they would call me.
Reported vs. Direct Speech: Key Differences
Tense Transformations
- Present Simple → Past Simple: “She says, ‘I work a lot'” → She said she worked a lot.
- Present Continuous → Past Continuous: “I’m reading” → He said he was reading.
- Present Perfect → Past Perfect: “I’ve eaten” → She said she had eaten.
Pronouns and Possessives
- “I” becomes “he” or “she”
- “My” becomes “his” or “her”
Time and Place Changes
- “today” → “that day”
- “tomorrow” → “the next day”
- “here” → “there”
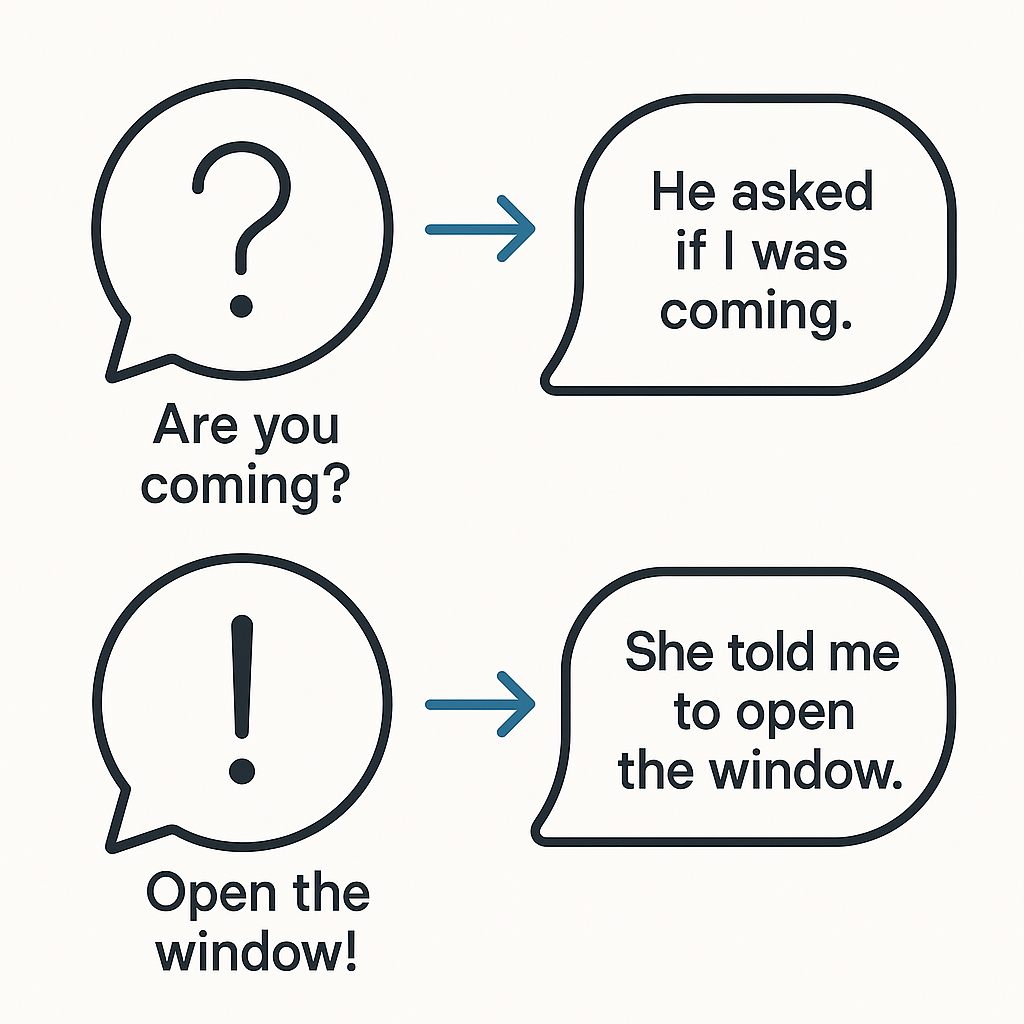
Questions in Reported Speech
- Question structure turns into statements.
- “Where is he?” → She asked where he was.
- Yes/No questions? Use “if” or “whether.”
- “Are you happy?” → He asked if I was happy.
Imperatives: Commands and Requests
- Use “to” + base verb.
- “Close the door” → He told me to close the door.
- “Please be quiet” → She asked me to be quiet.
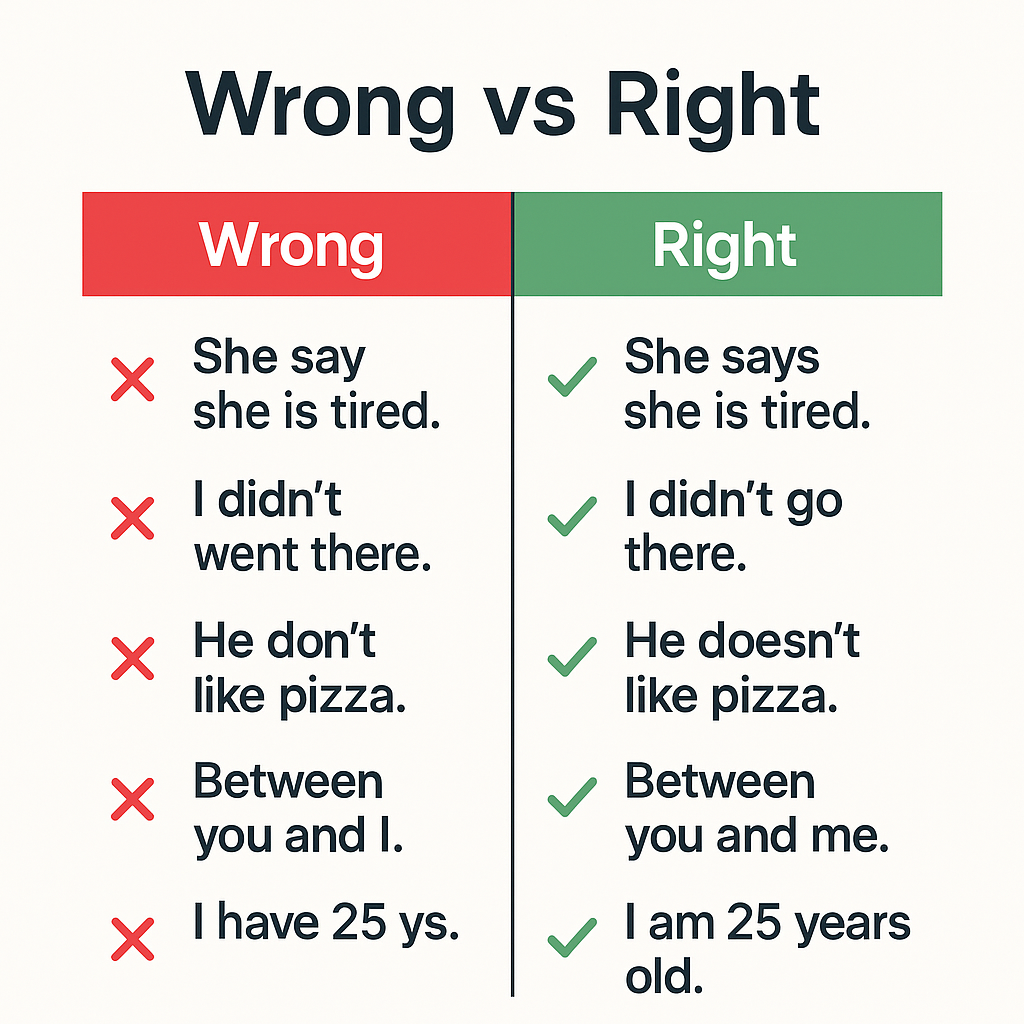
Mistakes to Avoid
- Keeping the tense unchanged. (You’re not special.)
- Using question word order in reported questions.
- Getting pronouns wrong and sounding like you’re talking to a ghost.
Related: The Simple Verb Tense – An In-Depth Overview
Also useful: Cambridge English Grammar Guide — a goldmine of trustworthy grammar resources that even your skeptical inner critic will approve.
Tense Shifts in Reported Speech (With Examples)
Here’s what this looks like in action:
- “I need help,” she said. → She said she needed help.
- “We’re going to the beach,” they said. → They said they were going to the beach.
- “Can you come early?” he asked. → He asked if I could come early.
Try these on your own:
- “I love pizza,” John said.
- “They are watching a movie,” she said.
- “Do you like this book?” he asked.
- “Don’t be late,” my mom told me.
- “Have you ever been to Paris?” she asked.
Answers:
- John said he loved pizza.
- She said they were watching a movie.
- He asked if I liked that book.
- My mom told me not to be late.
- She asked if I had ever been to Paris.
Also check out: What Part of Speech Is ‘And’? Understanding Parts of Speech
Why Bother?
Mastering reported speech not only makes your English sound smoother, it helps in writing, storytelling, and every time you want to gossip in a grammatically correct way.
Practice often, flex those verb tenses, and when in doubt — just blame the past tense. Oh, and while you’re at it, don’t miss our post on A Guide to the Simple Future Tense to complete your time travel training.
Ready to keep going? Dive into more language wisdom at our Grammar Blog.
FAQ
❓What is the easiest way to understand reported speech?
Think of it like retelling gossip, but politely. You don’t quote someone word-for-word — you paraphrase while adjusting grammar to match the context.
❓Why does the tense change in reported speech?
Because English loves drama. The tense changes to reflect that the event already happened when you’re reporting it.
❓Do I always have to change the pronouns?
Unless you want to accidentally say you fell in love with your boss instead of someone else, yes — change the pronouns.
❓How do I report yes/no questions?
Use “if” or “whether” before turning it into a statement. Example: “Are you ready?” → He asked if I was ready.
❓Is reported speech used in real life or just exams?
It’s everywhere — interviews, news reports, emails, and every family story that starts with “She told me that…”
